On this page we will look at some common terms and principles which are popular when we talk about electricity.
We will start with voltage, current and resistance. But before we talk about their relationship, let’s define them and understand what they are.
Voltage
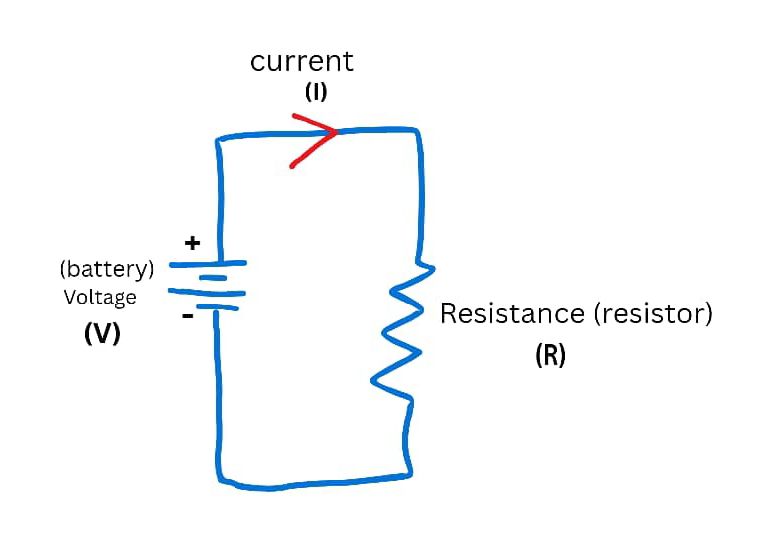
We can define voltage as the difference in electric potential (potential energy) between two points on a circuit. This difference results in electrical pressure that causes charged electrons to move in one common direction in a circuit.
This potential difference is what we term voltage. Voltage is measured in volts and is usually denoted by the letter V. The source of the potential difference can be a battery. Other common sources include solar panels, wind turbines, generators and electric sockets in our households via power stations.
Current
Curren can be defined as the flow of charged electrons in one common direction through conductive material in a circuit. The electrons flow from the negative terminal to the positive terminal, this is known as electron flow. This movement of electrons causes the movement of conventional current in the opposite direction, that is from positive to negative terminal.Therefore it can be said, without voltage we cannot have current.
Current is measured in amperes or simply amps. The symbol for amps is the capital letter A. That is the unit for current, example is 39 amps is written as 39A. The current itself is represented by the capital letter I in formulas and diagrams.
Resistance
Resistance can be defined as how much a material opposes the flow of electrical current. In other words how much it opposes the flow of charged electrons in a circuit. Resistance can be dependent on other factors such as the composition of the material( is it copper or silver), length, cross sectional area of the material and surrounding temperature. All these can have an effect on resistance.
Resistance is measured in Ohms. The symbol or unit for Ohms is Omega, represented by the omega sign Ω .
Resistors can be used to increase the resistance of a circuit. Resistors are usually used to get a desired outcome on the circuit. This is because of the relationship that exists between current, voltage and resistance. We will discuss this in the next topic.
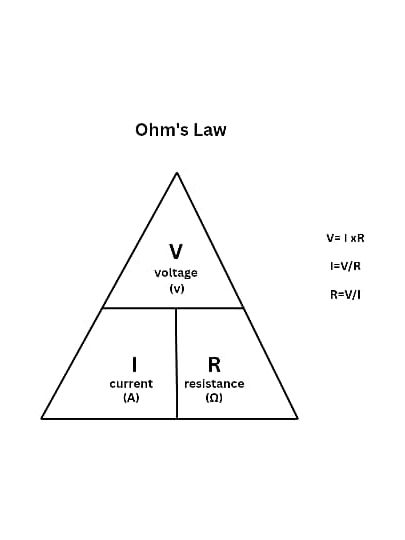
Ohm’s Law
The relationship between voltage, current and resistance can be understood as defined by ohm’s law.
Ohm’s Law states that, the electric current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage across it and inversely proportional to its resistance, as long as temperature and other physical conditions remain constant.
This can be seen by the formula:
V = I x R
Where V = Voltage, I = Current, R = Resistance.
From this formula we get
I = V/R , which is stated by ohm’s law
That is, Current is directly proportional to voltage and inversely proportional to resistance.
Simply put, Current increases as Voltage increases and Current decreases as Resistance increases.